UPPER CROSS SYNDROME
- Omkar Shirke
- Apr 22, 2022
- 4 min read
Updated: Apr 18, 2024
What is Upper cross syndrome?
Introduction
The kinetic chain describes the interrelated groups of body segments,
connecting joints, and muscles working together to perform movements and the
portion of the spine to which they connect. The perfect example of kinetic chain
is Upper Cross Syndrome. This type of syndrome refers to tightness in one area
leading to weakness in other areas, which can affect posture and overall joint
function and mobility.
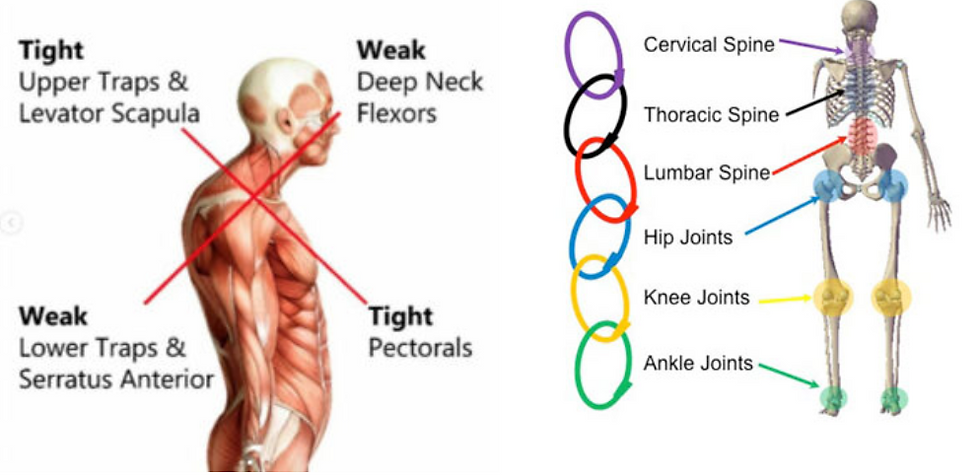
Upper cross syndrome is characterised by weakness in the deep neck muscles
and Shoulder blade muscles (lower trapezius and serratus anterior) while in the
tightness in the Upper trapezius and chest muscles (Pectorals) {1} .
What causes it?
Upper cross syndrome is most common in the people who have poor postures.
People who have prolonged sitting in front of laptop or desktop, prolonged
driving hours, watching TV, excessive cell phone browsing, or use of a texting
app, or game use, reading, biking are more prone to this syndrome.

The muscles of the neck and shoulders (upper trapezius, and levator scapula)
become extremely over activate. The muscles in the front of the chest (the major
and minor pectoralis muscles) become shortened, tight and inhibited .As a result
of these overactive muscles, the surrounding counter muscles overact. In this
syndrome, there is weakness in the muscles in front of the neck (cervical flexor
muscles) and in the lower shoulders (rhomboid and lower trapezius muscles) {1} .
What are the symptoms in Upper Cross Syndrome?
People with this syndrome have a lot of compensations in their which may
include slouched posture, rounded shoulders and a bent-forward neck.

The inhibited muscles put strain on the surrounding joints, bones, muscles and
tendons. A person having these compensation and mechanical imbalances may
experience symptoms including:
Pain in the neck, upper back, shoulders, Jaw, lower back region along with
tightness and pain in the chest at the intercostal region.
Some people with this syndrome may experience headache, fatigue, difficulty
in maintaining sustained postures like sitting to read or prolonged driving
hours {1} .
How to treat Upper cross syndrome?
The main aim to treat upper cross syndrome is to correct the mechanical
imbalances between the muscles which may include:
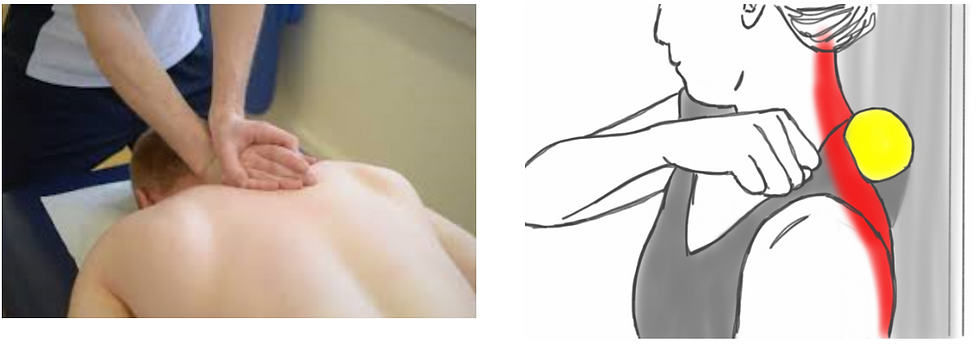
Releasing the tightness in the upper trapezius muscle and front chest muscles
(Pectorals) {2} .
Techniques like Deep tissue release, foam ball rolling, self-stretching, muscle
energy techniques needs to be included in the treatment process {3} .
Along with these techniques the strengthening of inhibited muscles like deep
neck flexors and working on scapular or shoulder blade muscles {3} .
Initially with the activation of these muscles and then progressing them with the
resistive bands considering their activities of daily living and the challenges
they face every day.
Include breathing exercise to improve Upper-chest expansion.

Exercises which include strengthening of scapular muscles


How to avoid Upper Cross Syndrome ?
The best way to avoid upper cross syndrome is to avoid prolonged postures
Break your postures every 30- 40 minutes. Avoid prolonged usage of cell
phone, limiting time spent watching TV, reading, using laptops and computers,
or driving.
Include cardiovascular exercise, ideally 30 minutes daily from low-impact
activities, such as walking or swimming.
Avoid faulty postures; do stretch the target tighter muscles of the back, neck,
shoulders, and chest. Follow proper ergonomics while doing the activities like
driving, do watch the position of the steering wheel, neck position while you
read a book, watch TV, or computer screen {4} .
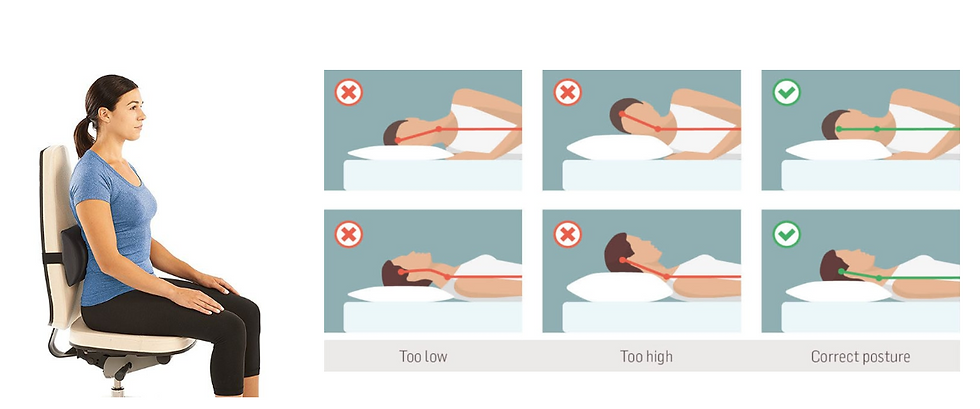
Make use of lumbar roll in chairs {5} , make use of the headset for long telephone
calls, and make use of a pillow which will support your neck while you sleep {6} .
While correcting the upper cross syndrome it is crucial to know the importance
of exercises, ‘Strengthen and stretch’ should be the motto while dealing with
upper cross syndrome. Avoiding faulty postures and having a habit of breaking
the sustained postures will help in prevention and faster recovery.
References:
1] Moore MK. Upper crossed syndrome and its relationship to cervicogenic
headache. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2004;27(6):414‐420.
doi:10.1016/j.jmpt.2004.05.007.
2] Bae WS, Lee HO, Shin JW, Lee KC. The effect of middle and lower
trapezius strength exercises and levator scapulae and upper trapezius stretching
exercises in upper crossed syndrome. J Phys Ther Sci. 2016;28(5):1636‐1639.
doi:10.1589/jpts.28.1636.
3] Arshadi R, Ghasemi GA, Samadi H. Effects of an 8-week selective corrective
exercises program on electromyography activity of scapular and neck muscles
in persons with upper crossed syndrome: Randomized controlled trial. Phys
Ther Sport. 2019;37:113‐119. doi:10.1016/j.ptsp.2019.03.008.
4] Baker R, Coenen P, Howie E, Williamson A, Straker L. The Short Term
Musculoskeletal and Cognitive Effects of Prolonged Sitting During Office
Computer Work. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2018;15(8):1678. Published
2018 Aug 7. doi:10.3390/ijerph15081678.
5] Horton SJ, Johnson GM, Skinner MA. Changes in head and neck posture
using an office chair with and without lumbar roll support. Spine (Phila Pa
1976). 2010;35(12):E542‐E548. doi:10.1097/BRS.0b013e3181cb8f82.
6] Jeon MY, Jeong H, Lee S, et al. Improving the quality of sleep with an
optimal pillow: a randomized, comparative study. Tohoku J Exp Med.
2014;233(3):183‐188. doi:10.1620/tjem.233.183

Comments